Quantification of ligand binding in live cells
THE PRINCIPLE
While our BBV based ligand binding assays make ligand binding studies convenient, it is beneficial to validate these results using live-cell assays or to repurpose fluorescent ligands which are not suitable for fluorescence anisotropy assays due to restrictions of fluorescence lifetime or size of the fluorescence ligand.
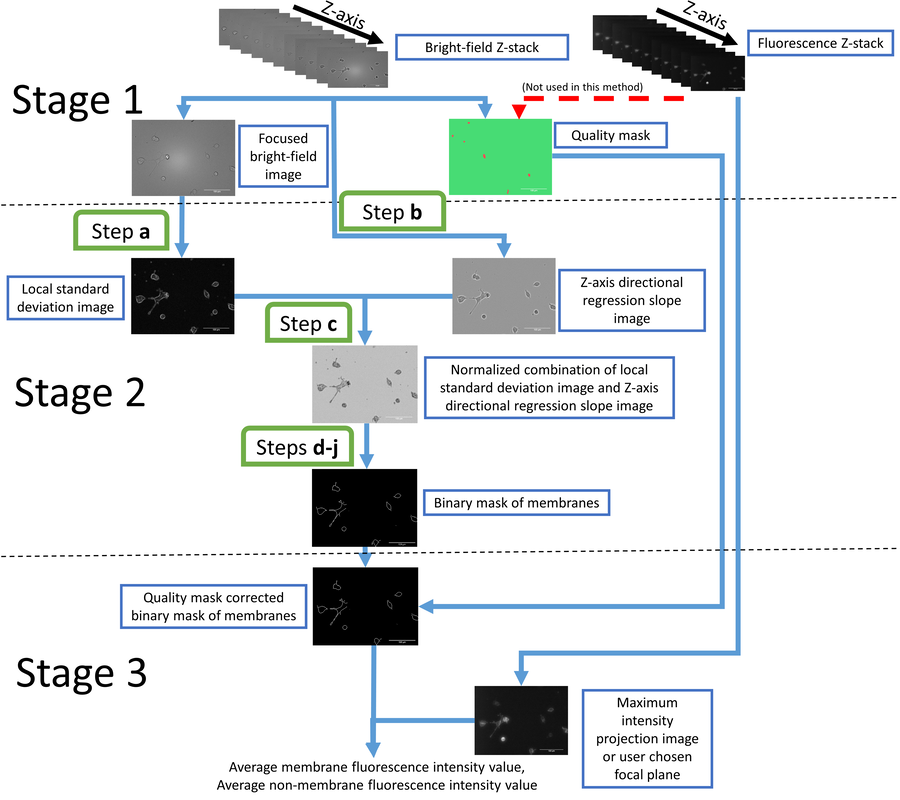
We have developed a method that uses a combination of automated widefield fluorescence and bright-field microscopy. The cells are imaged from multiple Z-planes and a machine-learning based algorithm finds either the cell membrane or the entire cell cytosol. The fluorescence signal from only the location of the detected pixels is integrated and represents the extent of fluorescence ligand binding to these cells. The method can be used to measure the affinity of the fluorescent ligand or use the fluorescent ligand in competition with unlabeled ligands. The method can also be used to determine ligand binding kinetics of the fluorescent ligand. The algorithm is implemented as an Aparecium tool Membrane Tools and is distributed as an open source software. The method has been validated using a novel D3 fluorescent ligand NAPS-Cy3B. Link to full text publication.
We have developed a method that uses a combination of automated widefield fluorescence and bright-field microscopy. The cells are imaged from multiple Z-planes and a machine-learning based algorithm finds either the cell membrane or the entire cell cytosol. The fluorescence signal from only the location of the detected pixels is integrated and represents the extent of fluorescence ligand binding to these cells. The method can be used to measure the affinity of the fluorescent ligand or use the fluorescent ligand in competition with unlabeled ligands. The method can also be used to determine ligand binding kinetics of the fluorescent ligand. The algorithm is implemented as an Aparecium tool Membrane Tools and is distributed as an open source software. The method has been validated using a novel D3 fluorescent ligand NAPS-Cy3B. Link to full text publication.
|
Saturation binding of NAPS‐Cy3B binding to live HEK293‐D3R cells. The HEK293‐D3R (20000 cells/well) were incubated with two‐fold serial dilutions of NAPS‐Cy3B in the range of 0–8 nm and with (nonspecific binding, blue) or without (total binding, red) 1 µm (+)butaclamol. The background corrected membrane fluorescence intensities are determined by the membrane detection algorithm as described in Materials and Methods and presented as mean ± SEM from pooled data of three independent experiments performed in duplicates. Four images from different fields of view were taken from
a single well. |
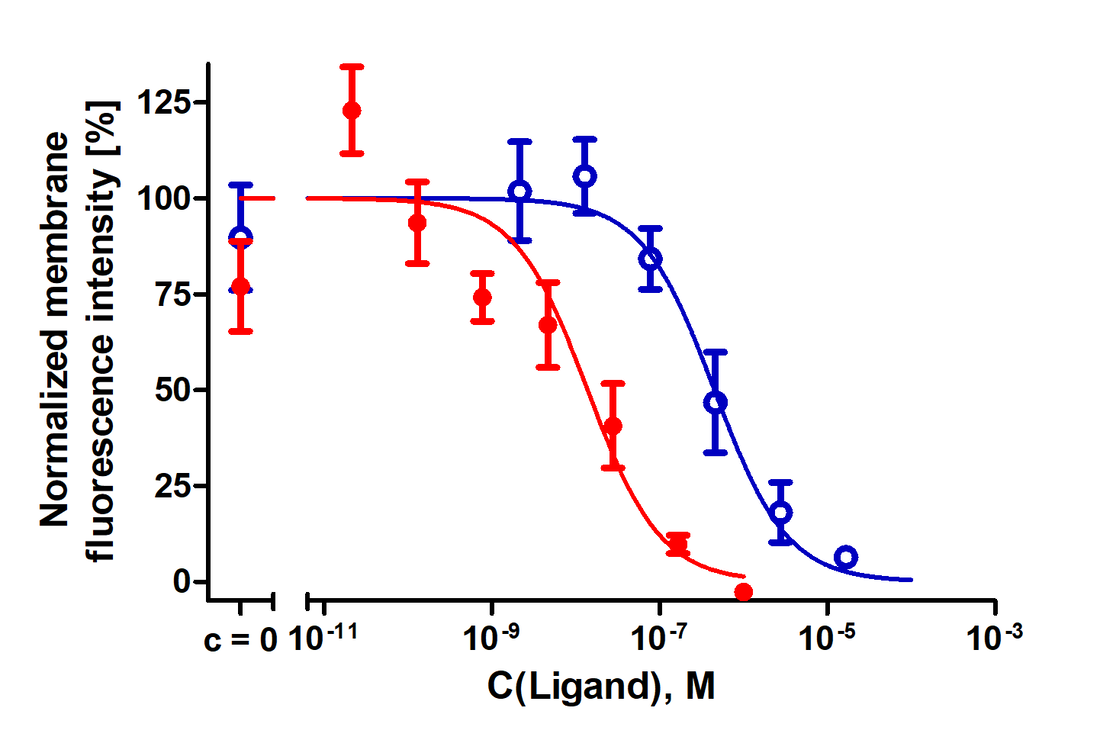
Inhibition of NAPS‐Cy3B binding to live HEK293‐D3R cells by dopaminergic ligands. The HEK293‐D3R (20 000 cells/well) were incubated with 1 nm NAPS‐Cy3B and different concentrations of dopamine (blue) or (+)butaclamol (red) for 90 min as described in Materials and Methods. The membrane fluorescence intensities are determined by the membrane detection algorithm and presented as mean ± SD from a representative experiment performed in duplicates. Four images from different fields of view were taken from a single well. Data have been normalized to lower and upper plateau values of 0% and 100%, respectively.
|